Quick Guide
Get up and running with wsgrok in minutes
The essential guide to installing, authenticating, and using the wsgrok tunneling client.
Table of Contents
1. Installation
Install the wsgrok client agent on your local development machine using our automated installers or manual download.
Linux / macOS
curl -sSL https://wsgrok.com/install.sh | bash
Windows (PowerShell)
iwr https://wsgrok.com/install.ps1 | iex
2. Authentication
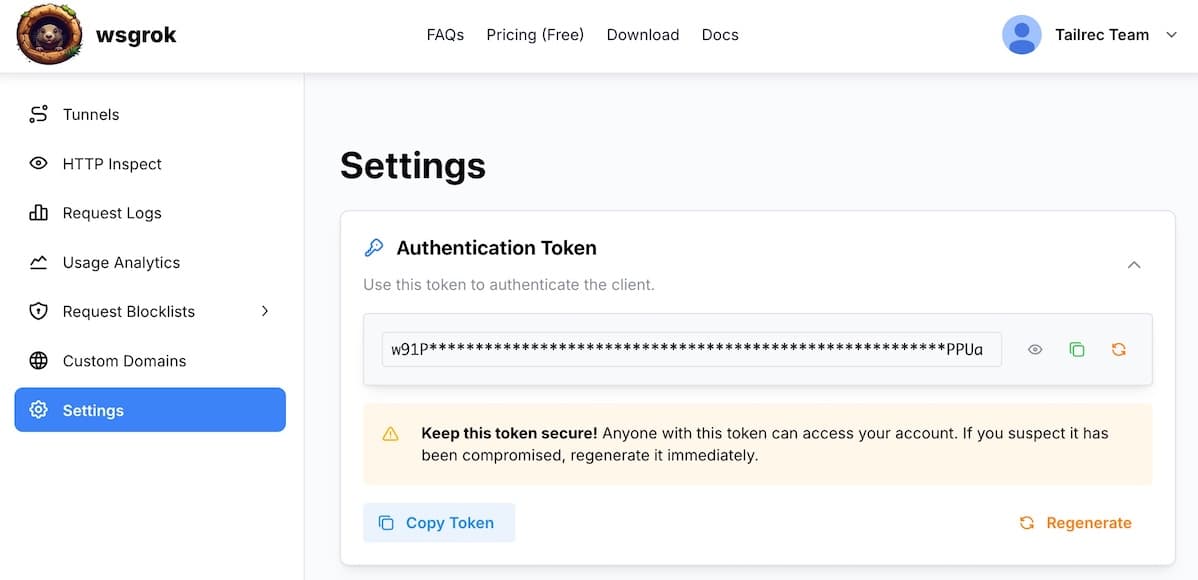
Before establishing a tunnel, you must link your CLI client with your wsgrok account using your personal authorization token.
Steps to Authenticate:
- Login to the wsgrok Console.
- Navigate to your Profile settings.
- Copy your unique Authorization Token.
- Run the setup command in your terminal:
wsgrok --auth
Paste your token when prompted. The client will securely store it in your home directory.
3. Basic Usage
Starting a tunnel is simple. You just need to specify the local port and your desired subdomain.
Command Syntax:
wsgrok <port> <subdomain>
Real-world example:
wsgrok 3000 my-cool-app
This creates a secure tunnel from https://my-cool-app.region.wsgrok.com directly to your local service running on port 3000.
4. CLI Reference
The wsgrok client supports several flags for advanced configuration and performance tuning.
| Flag | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
-subdomain | The subdomain to use for the tunnel | -subdomain api |
-port | Local port to tunnel | -port 8080 |
-connections | Number of parallel connections (1-4, default: 2) | -connections 4 |
-client-id | Custom identifier for this client instance | -client-id worker-1 |
--auth | Trigger authentication token setup | wsgrok --auth |
--version | Display version and build information | wsgrok --version |
5. Tunnel Management
While the CLI agent handles the traffic, the wsgrok Web Console provides advanced management and observability tools.
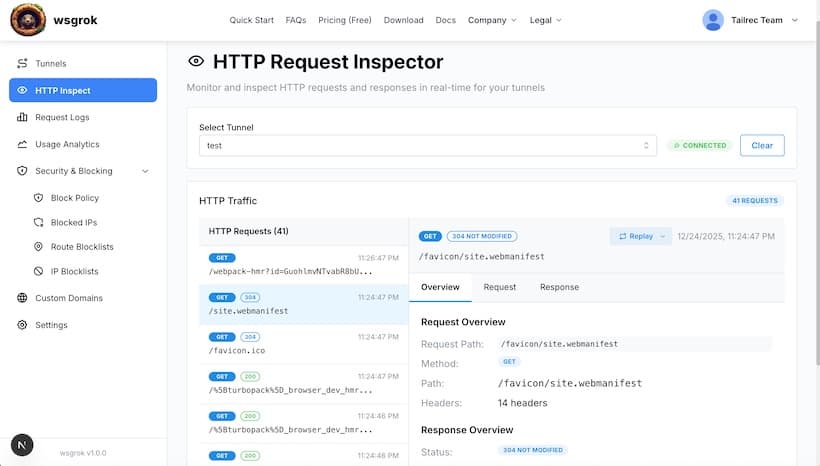
HTTP Inspection
Monitor and debug HTTP traffic in real-time. View headers, body payloads, and response codes. You can even replay requests to test your local service.
Security Controls
Configure IP whitelists, route blocklists, and global policies. For more details, see our Security Configuration Guide.
Summary
You're now ready to use wsgrok! Remember that your tunnel remains active as long as the CLI process is running. To stop the tunnel, simply press Ctrl + C in your terminal.
Looking for more technical details?
Read the Architecture Whitepaper